Just when you do a relief stretch after launching a website update, it comes to your attention that a logo is slightly misaligned, and worst of all, text is overlapping on different browsers. It happens far more often than developers admit. An unnoticed change in your code can cause major visual bugs that ruin the user experience.
The rise of such risk is why visual regression testing is no longer optional. It is a fundamental necessity for any team aiming for continuous quality. This essential QA method helps preserve the delicate integrity of your design and the crucial consistency of your brand. It directly impacts user trust and conversion rates. It ensures that every new code deployment keeps the user experience exactly as it should be.
This guide will explain exactly how visual regression testing works. We will explore the difference between pixel-perfect checks and checks for perceptual differences. You will learn how automated systems can catch subtle changes that the human eye often misses, so you can master UI testing automation and achieve flawless cross-browser testing.
What Is The Meaning of Visual Regression Testing?
Visual regression testing is a quality assurance process that checks that a software’s interface hasn’t changed unexpectedly after updates.
Instead of checking functionality, it checks how things look. It does this by taking screenshots before and after changes and automatically comparing them to spot any differences in UI design or elements across browsers and devices.
The core idea centers on snapshot testing. You take a baseline image of your User Interface (UI) before the update. Then, after every code change, the system captures a new snapshot to perform a visual diff between the old baseline and the new image. If the difference, called a visual bug, is detected, the test fails and alerts the team.
Tired of Broken Layouts?
Our advanced visual testing stops layout failures and saves review time.
Book Your Slot NowHow Visual Regression Testing Differ from Functional Regression Testing?
Traditional functional regression testing checks if features still work. For example, it ensures a login button still logs a user in. It focuses on logic and behavior.
Visual regression testing checks if features still look right. A button may still log you in, but if its color changed from blue to red without permission, only visual testing will flag that issue. Functional testing does not care about all such visually appealing placements.
Here is the easiest way to comprehend the difference. Regular testing confirms the engine runs. Visual testing confirms the car still looks like a sports car. Both are vital for a complete and robust continuous quality pipeline. It is a shift from purely checking back-end development logic to actively preserving front-end design integrity.
Types of Visual Regression Testing
Visual regression testing (VRT) checks for unexpected changes in a user interface by comparing it to a reference version. There are different kinds of VRT, based on how the comparisons are done and how automated the process is.
The following are the common VRT techniques used to compare UI snapshots.
Pixel-by-Pixel (fast but sensitive)
It compares every single pixel of the new snapshot against the baseline image. This method is fast but overly sensitive. It fails if even a single pixel color changes, often leading to many false positives. This approach provides a very strict visual diff but needs constant maintenance due to minor rendering differences across devices.
DOM-Based (structure-level)
It inspects the structure of the DOM tree and its associated styles instead of pixel colors. This approach is more resilient to slight rendering shifts and better at catching structural issues. It ensures elements are correctly positioned in the code structure. This is useful for component testing but can miss purely visual problems that do not alter the underlying code structure.
AI-Driven VRT (human-like accuracy)
It uses machine learning to mimic human vision and assess perceptual differences on the screen. By understanding layout structure and the purpose of each element, the system drastically reduces false positives caused by minor visual noise—an approach commonly implemented through advanced Machine Learning Development Services.
It often uses a dynamic content masking technique to ignore changing areas like ads or timestamps. This approach offers human-like accuracy and requires far less baseline management, making it the modern standard for scaled testing.
| Technique | Pros | Cons | Tools |
| Pixel-by-Pixel | Simple, fast execution, highly accurate for exact copies. | Extremely sensitive to minor shifts, with high false positives. | Puppeteer, Selenium, BackstopJS |
| DOM-Based | Handles minor rendering shifts better; less sensitive to environmental noise. | Misses actual style shifts or purely visual errors. | Cypress, Playwright, Storybook |
| AI-Based (Perceptual) | Ignores noise and minor shifts, drastically reduces false positives. | Higher tool cost, potentially steeper learning curve. | Applitools, Percy, LambdaTest |
Underlying Importance of Visual Regression Testing
Why should you prioritize automated visual regression testing? The answer connects directly to business performance and user retention. Visual consistency builds trust. Broken UIs confuse customers and drive them away, directly impacting conversions and revenue.
Below, we explain why automated visual regression testing is crucial for your business and how it saves time and money.
Spots Missed Bugs
As developers mainly focus on functionality and manual QA testers tire quickly, subtle visual changes are often missed. Automated processes can catch minuscule shifts in padding, alignment, or font rendering across hundreds of pages and devices—something nearly impossible to do manually. This is especially critical for teams working with an experienced Ecommerce App Development Company, where even minor visual inconsistencies can directly impact user trust and conversions. One of our clients, a large e-commerce platform, discovered that 15% of their user complaints were linked to visual bugs that functional tests failed to detect.
Ensures UI Consistency
Your brand identity relies on a cohesive and consistent visual presentation. A change in the CSS file for one component can accidentally affect the spacing of another on a different page. Visual regression testing ensures your design system standards are enforced everywhere. This is particularly important for large applications using component libraries like visual regression testing React components.
Prevents Regression
It’s another main benefit of VRT. The new feature can accidentally break other parts of the interface. Through visual regression testing with a trusted baseline image, the organization spots these issues right away. This saves countless hours that would otherwise be spent troubleshooting issues reported by angry users.
Integrates with CI/CD
Adding visual regression testing into the Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery (CI/CD) pipeline helps catch visual issues earlier in the software development process.
Every code push is automatically checked. If the visual check fails, the deployment stops, preventing visual defects from ever reaching a staging or production environment. This tight integration ensures rapid feedback and promotes faster development cycles to practice true agility.
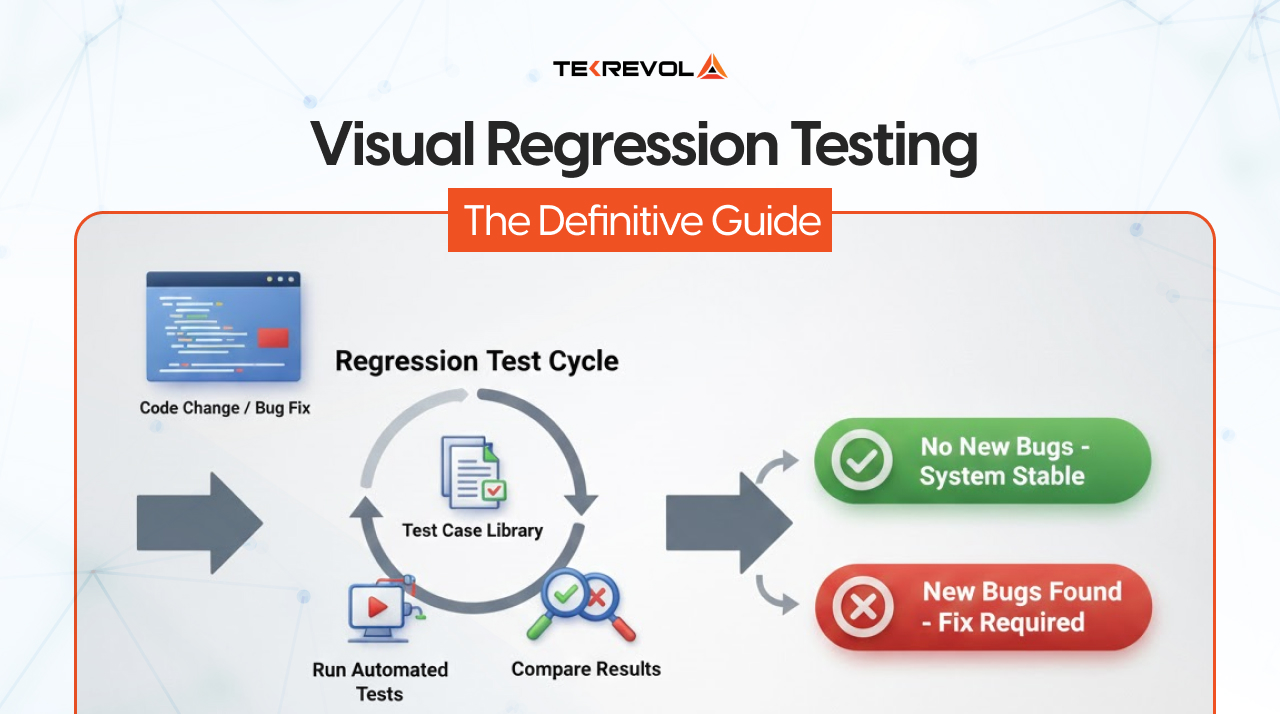
How to Conduct Visual Regression Testing?
Implementing visual regression testing involves a clear, repeatable cycle. This process ensures reliability and manages the massive volume of data generated by comparing multiple pages across multiple browsers. Below, we walk through the four steps of the standard testing workflow.
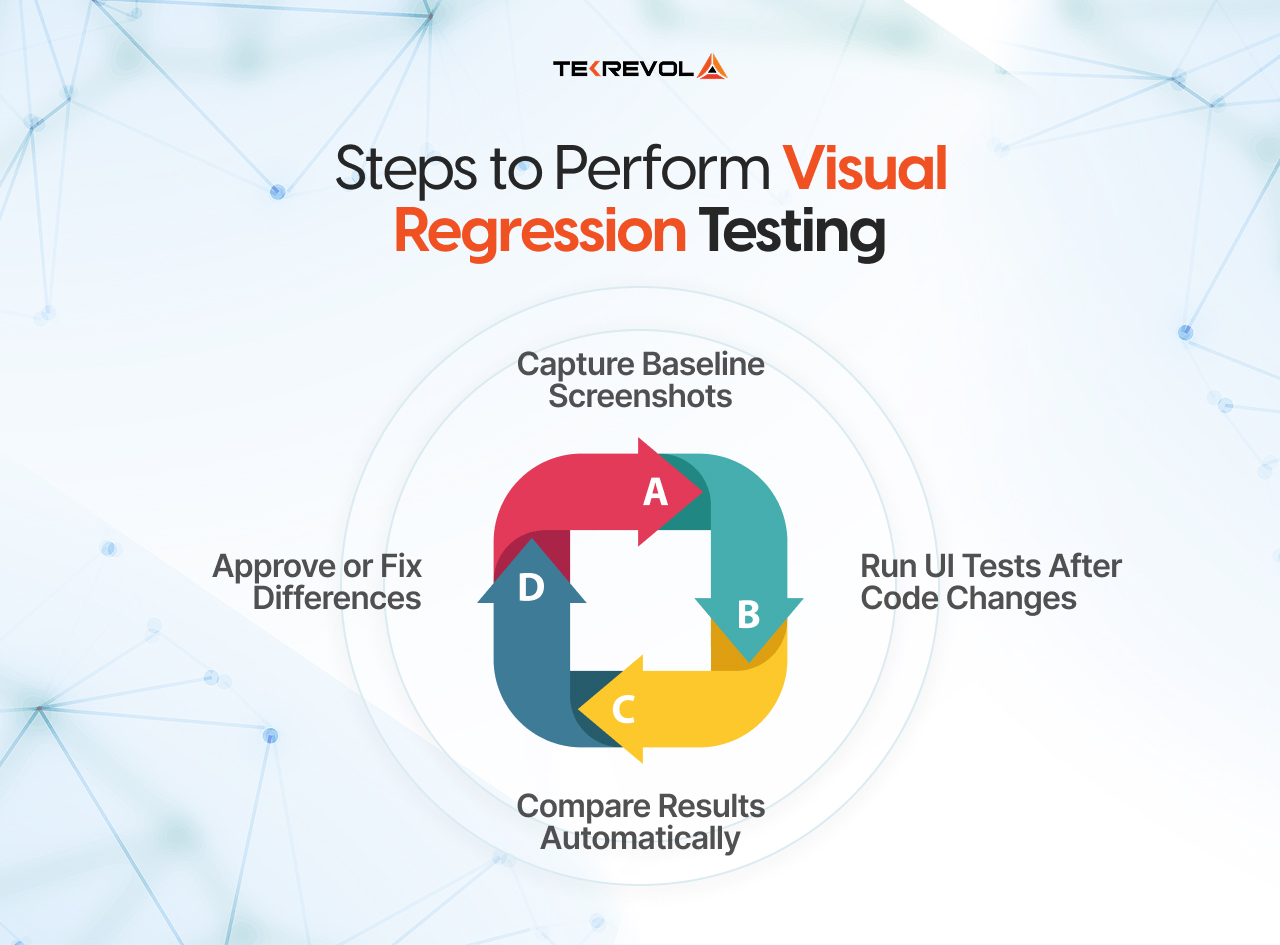
1st Step: Capture the Snapshots
Your selected automation testing tool visits the page and takes a snapshot. For bigger or more complex pages, it usually combines multiple screenshots to create a complete view of the page. This snapshot is essentially the raw data for the visual check.
2nd Step: Define the Baseline
The very first snapshot captured from a known, stable version of the UI becomes the baseline image. This image is stored securely, often in a dedicated visual testing platform or repository. This baseline represents the single source of truth for what the UI should look like.
3rd Step: Run the Comparison (Visual Diff)
When a developer submits new code, the system reruns the test to capture a new snapshot. That new image is sent to a comparison engine, which then performs a visual diff against the stored baseline. The result is typically a diff image that highlights the pixels or areas that have changed.
4th Step: Review and Update the Baseline
Here, tools and the human work in the loop. If the test fails, the QA expert or developer reviews the difference in nature, which usually falls into these categories.
- If the difference is an unintended visual bug, app developers fix the code and run the test again, a workflow commonly followed by an experienced app developer in DC to ensure visual accuracy before release.
- For an intentional change (e.g., a planned UI redesign), the reviewer approves the change. This new snapshot then officially replaces the old one to establish the updated baseline.
This review and update cycle is the heart of maintaining an accurate and reliable visual regression testing software setup. It prevents good changes from causing failures and keeps the test suite relevant.
Stuck in the Review Cycle?
Our smart system handles baseline updates and removes manual approval friction.
Request a DemoBest Visual Regression Testing Tools For 2025
Visual regression testing tools are evolving from simple open-source libraries into powerful AI-driven cloud platforms. Choosing the right software depends on your team’s technical expertise, budget, and the scale of your application—often with guidance from experienced cloud consulting services to ensure the tools align with long-term infrastructure and testing goals.
Here is a look at some of the leading solutions available for 2025.
| Tool | Highlights | Pricing Model | Unique Feature |
| Applitools Eyes | Uses sophisticated Visual AI for high accuracy and low false positives. Excellent for large enterprise applications. | Subscription-based, based on the number of snapshots. | Root Cause Analysis identifies the exact CSS/DOM change that caused the visual difference. |
| Percy (Browser
Stack) |
A specialized platform for automated visual regression testing. Highly scalable, excellent user interface for baseline review. | Subscription-based. Offers a generous free visual regression testing tools tier. | Integrates deeply with popular frameworks and offers built-in cross-browser testing. |
| LambdaTest (Smart UI) | Cloud-based platform offering massive parallelism for faster execution. Strong focus on comprehensive browser coverage. | Tiered subscription. | Smart UI testing that reduces baseline maintenance overhead. |
| BackstopJS | A popular visual regression testing open-source framework. Simple to set up, uses PhantomJS or Chrome Headless. | Free | Highly customizable configuration settings for different screen sizes and environments. |
| Cypress | While primarily a functional tool, extensions like Cypress visual regression testing add robust snapshot capabilities directly into the test suite. | Free (core framework). | Deep integration with the Cypress environment makes it fast for developers. |
For organizations serious about quality, investing in a tool with visual AI capabilities is transformative. The cost is often offset quickly by the reduction in maintenance time and the elimination of expensive production-level visual bugs.
When to Run Visual Regression Tests?
The “when” is just as important as the “how.” For most modern teams delivering a professional web development service, visual regression testing should be integrated into every stage of the software lifecycle. Below are some of the ideal moments to run these checks within your development cycle.
Continuous Integration (CI)
The most important time to run these tests is when code is committed or merged. This process, called Continuous Integration (CI), ensures the code has not introduced any unintended visual bugs before it moves forward. Running the full checks nightly is a standard practice for comprehensive coverage.
Before Releases
Before you finalize a release, always run a full set of visual and cross-browser testing checks as a safety net. It confirms the entire application looks exactly right across every device and browser you target. This final, critical check prevents regressions from making it into the hands of your users.
After UI Redesigns
When your team works on a significant UI overhaul or component library update, running these tests is crucial. They will quickly highlight any pages that were missed or elements that did not adopt the new styles correctly. This is where the sheer volume of visual regression testing excels compared to manual checks.
Tie into Agile Sprint Cycles
Within an agile framework, testing is continuous. As soon as a feature is complete, it is tested both functionally and visually. This early and frequent testing ensures defects are discovered when they are cheapest to fix. Teams often focus their visual regression testing on components impacted during the current sprint, an approach that strongly supports rapid iteration when delivering MVP Development Services.
Visual Regression Testing Challenges and Best Practices
Performing visual regression testing is not without difficulties. The main hurdle is dealing with dynamic content and ensuring tests run efficiently without generating too many noise alerts. Learn how to overcome common hurdles like false positives and dynamic content.
False Positives
Dynamic content is the biggest enemy of visual testing. Timestamps, live stock tickers, rotating ads, or personalized user names will cause the page to change on every run.
Best Practices
- Use mechanisms provided by your visual regression testing software to ignore specific regions of the page. Tools allow you to mask or hide elements before the snapshot is taken, maintaining a dynamic baseline strategy.
- Wait for the page to be completely stable before taking the snapshot. This prevents failures caused by in-flight animations or late-loading elements.
Slow Integrating with CI/CD
Successful visual regression testing requires seamless CI/CD integration. This means the tests must be fast and reliable enough to run on every commit. If the visual suite takes an hour to run, developers will ignore it.
Best Practices
- Leverage cloud-based tools commonly used in cloud application development services that enable parallel testing to distribute the workload and complete executions in minutes.
- Run tests only on affected components or pages in pre-merge checks, saving the full suite for nightly runs.
Overload Baselines
The more pages you have, the more baselines you have to maintain. When you do a global font change, thousands of baselines may need to be approved simultaneously.
Best Practices
- Treat the baseline image repository like code. Use proper version control and ensure every update is tracked and approved.
- Use intelligent grouping in your tool so that large, intentional changes can be approved with a single click rather than one by one.
Conclusion
Visual regression testing stands as the ultimate guardian of your User Experience. It is the safety net that ensures the hard work of your design and development teams remains intact with every new deployment.
By implementing sophisticated automated visual regression testing, you guarantee consistency, build customer trust, and ultimately protect your brand’s reputation.
If you are looking to fully integrate these techniques or require a specific platform tailored to your unique application structure, contact TekRevol. We provide custom software solutions designed for your codebase to help you accelerate your journey.
Ready to Upgrade Your QA Process?
See how our AI-powered visual testing platform outperforms competitors.
Book Your Free Call