Healthcare data now drives everything from remote patient monitoring to telehealth consultations, but with this convenience comes immense responsibility. Protecting sensitive patient information isn’t just good practice; it’s essential for healthcare data security, user trust, and legal compliance.
When a healthcare app development company creates products with secure features, they are not only writing code. They are designing systems that safeguard lives and privacy at scale. In this blog, we’ll explore exactly how app developers implement encryption and safety for medical data, offering a detailed, practical view of the process.
What Developers Mean by Medical Data in Healthcare Applications
For companies creating a medical app, such data isn’t just another piece of information. PHI refers to any health-related information that is combined with identifiable data, such as medical records, diagnoses, prescribed medications, therapy or treatment details, laboratory test results, DNA/genetic information, biometric data, insurance, and any other information that can be directly linked to an individual.
Such information is very tightly controlled, very sensitive, and definitely a top target of cybercriminals.
Actually, healthcare data breach cases keep increasing every year, with patient data of hundreds of millions being exposed in recent cases.
According to HIPAA breach reports, more than 846 million medical records were exposed from security breaches and leaks between 2009 and 2024. And that number is over 2.6 times the population of the U.S.
The scale of these breaches highlights the importance of data security in healthcare more than ever. Just looking at recent years, healthcare app development company in the United States reported hundreds of large-scale data incidents impacting millions of records.
Why This Matters for Developers
A mobile app development company and its team must understand the nature of this data because it defines how they design, store, encrypt, transmit, and control access to every piece of information touched by their applications. Healthcare app security requires more than normal privacy measures; it demands industry‑standard encryption and safety practices baked into every layer of the system architecture.
Healthcare apps demand stronger security
Tekrevol helps you build encryption-first solutions that scale safely.
Get your free consultationHow Medical Data Moves Within an App Ecosystem
Before developers write any code, they map out how data flows throughout the application. Understanding the journey of medical data is essential for determining the points of vulnerability.
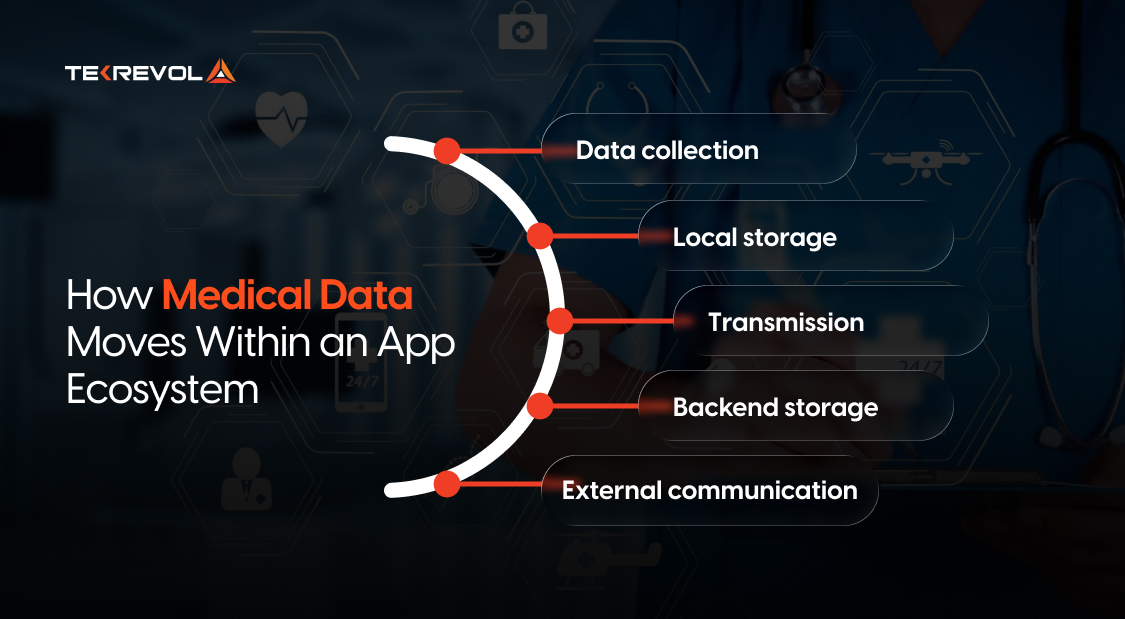
Every piece of medical information in an app flows through several touchpoints:
- Data collection: when a user enters health details, measurements from a wearable, or symptom inputs.
- Local storage: data stored on the mobile device before syncing with a server.
- Transmission: data sent between the app and remote servers or third-party services.
- Backend storage: secure servers or cloud databases that house PHI.
- External communication: information exchanged with Electronic Health Record (EHR) systems, laboratories, insurers, or analytics services.
By mapping this flow, developers can clearly see exactly where encryption, access control, and monitoring will be necessary. It also helps in foreseeing risks like insecure APIs or mishandling of third-party integrations. If you are a beginner, you can also learn about API development and the challenges a developer faces.
Data Collection Points in Healthcare Apps
Developers carefully define how and where data is collected. For instance:
- User-input forms for health history or symptoms
- Some of the data sources can be your various health monitoring devices e.g. heart rate monitors, glucose tracking devices, or even smart watches.
Telehealth sessions record various data such as video, audio, and chat logs.
In all these different places where data is gathered, top telehealth app development companies ensure every security measures should be in place for data protection to
Storage and Data Management
Data, once collected, can either be held briefly on the device prior to sending it or be saved permanently in backend systems. Programmers encrypt databases, files, and logs at rest, at the same time implementing strict server-side protections.
Besides that, cloud storage providers normally showcase additional encryption and monitoring features; however, it is the developers’ responsibility to make sure that mobile app security is a top priority for users.
Data Sharing With External Systems
Today, healthcare apps are frequently connected to APIs, EHR systems, labs, and insurance providers. It is essential that developers ensure the security of these links by using encrypted channels, API tokens, and implementing highly restrictive access control policies so as to avert any kind of unauthorized disclosure or alteration of data.
Encrypting Medical Data at Rest
One of the biggest priorities in mobile healthcare development is ensuring that when data is stored, whether on the device or on a server, it remains encrypted and inaccessible to unauthorized parties. This all happens with the help of big data encryption and methods.
Why Data At Rest Needs Encryption
Data “at rest” refers to information that is not actively being used or transmitted. On a mobile device, this includes databases, files, caches, and logs. On a server, this covers databases and backups.
If this data were ever accessed by attackers, for example, through unauthorized file extraction, device theft, or a breached server, encryption ensures it remains unreadable without the proper decryption keys.
Industry Standards Used by Developers
Developers commonly use trusted algorithms like:
- AES‑256 for database encryption
- System‑level secure storage on mobile devices (iOS Keychain, Android Keystore)
- Encrypted file systems for backups and archives
These methods turn plain text data into ciphertext, which is unreadable without corresponding decryption credentials. By encrypting data at rest, developers are building a strong first line of defense. Furthermore, do you know that Statista reported that the most significant healthcare breach resulted in fewer than 100 million data records from Change Healthcare’s database?
Data security isn’t optional in healthcare
Tekrevol aligns your app with modern encryption standards.
Claim your free strategy callEncrypting Medical Data in Transit
Medical data is constantly moving, from app to server, server to provider, and sometimes between services. When developers think about data security for healthcare, they focus just as much on secure transmission as they do on secure storage.
Why Transmission Encryption Matters
If sensitive information like health records or identifiers are sent in clear text over a network, hackers can intercept that data using common attack vectors like packet snooping or man‑in‑the‑middle techniques. Securing this transmission is absolutely necessary to prevent unauthorized access.
Protocols and Approaches Used
Developers enforce secure data transfer using:
- HTTPS/TLS 1.2+ encryption to secure all API requests and responses
- End‑to‑end encryption for sensitive exchanges between endpoints
- Sometimes a bad guy tries to lure you to a fake website.
Certificate pinning makes sure that the server you’re connected to is genuine and not a bad guy. This way, the bad guy won’t be able to intercept your traffic and steal data.
The above measures are designed so that even if an attacker manages to get in between the communication, the data will still be secure, and no one without the correct decryption keys will be able to read it.
It’s a very important step, especially considering that a good number of hacking cases are initiated from compromised or insecure networks and badly protected channels of data transmission.
Keeping Encryption Keys Secure
Encryption alone is not enough; it has to be ensured that the keys that are used to protect the encrypted data are also secured properly.
Importance of Key Management
Encryption keys have the greatest impact on whether the encrypted data stays secure and is inaccessible to unauthorized users or if it can be read by them. Even the strongest encryption algorithm is nothing if keys are stored insecurely or are mishandled.
Developers follow best practices for key security by:
- Using dedicated key management services
- Separating keys from the encrypted data storage
- Rotating keys on a schedule to reduce the risk of exposure
- Controlling key access with strict policies and auditing
Key management isn’t just another checkbox; it’s central to how encryption works in practice for medical data. With such measures, you can easily protect data in multicloud architecture.
Authentication and Access Control for Medical Data
Encryption alone doesn’t stop someone with access privileges from viewing protected information. This is where authentication and access control become essential layers of defense.
Role‑Based Access Control (RBAC)
Developers implement systems where users are only given the permissions they absolutely need. For instance:
- Patients can view their own records
- Physicians can access records for their patients
- Admins might have broader oversight capabilities
This minimizes risk if credentials are compromised and ensures that even internal users cannot access more data than necessary.
Authentication Techniques Used
To strengthen user identity verification and protect medical data:
- Multi‑factor authentication (MFA) is used to confirm identities
- Secure session management prevents hijacking
- Timeouts prevent stale sessions from risking exposure
These controls assist in preventing any unauthorized access and that is only part of the reason why healthcare data security is considered to be much more comprehensive than the usual app security implementations.
Make sure that there is Minimal Data Exposure
Occasionally, the most effective security measure is simply being aware of what you should not store.
Developers designing data security for the healthcare sector are always aware that they are limiting the amount of sensitive data that they are collecting and keeping. This concept of data minimization means:
- Collect only what the app needs
- Discard sensitive data when no longer necessary
- Avoid redundant copies of health records without a reason
Doing less with data often reduces risk and ensures developers don’t inadvertently expose more information than required.
Consent Management and Privacy Controls
Patient consent isn’t just ethical, it’s a legal requirement.
Developers must build systems that enforce user consent at multiple stages:
- Asking for permission before accessing or sharing PHI
- Providing users control over how their data is used
- Allowing users to revoke consent or request deletion of their data
This isn’t just about satisfying a legal requirement; it strengthens trust between users and the app.
Compliance‑Driven Security Practices
Apps that promote healthcare on the go have to live up to safety regulations more strictly than almost any other mobile apps in the world. Those who create these apps need to develop such systems that are not only secure but also compliant.
Some of the most important directives from the regulatory bodies highlight:
- Encryption of PHI during transit and while being stored
- Using monitoring and logging to identify security breaches
- Putting in place technical safeguards such as authentication and access control
Security without compliance is incomplete. Developers balance technical measures with regulatory expectations to ensure apps are not only secure but also legally sound.
Securing APIs and Third‑Party Integrations
Modern healthcare applications rarely operate in a vacuum. They exchange data with external services like labs, insurance systems, EHRs, and analytics platforms using APIs.
Developers secure these integrations by:
- Using secure API keys and tokens
- Employing strict authorization mechanisms
- Validating data inputs to prevent injection attacks
- Monitoring API usage for abnormal patterns
When done correctly, API security becomes a crucial part of healthcare data security, ensuring that every handshake between systems is authenticated and encrypted.
Ongoing Monitoring, Testing, and Incident Preparedness
Healthcare data security isn’t a one‑time task. Developers adopt a lifecycle approach that includes:
- Regular security testing and audits
- Vulnerability scanning
- Penetration tests
- Incident response planning
Hence, threats are identified and eliminated without users feeling their impact, and developers are equipped to deal with the consequences of a breach if it happens.
Healthcare Data Security Challenges Developers Address
Developers in the digital health sector are at the forefront of battling some of the most severe problems of data security in healthcare. They must not only counter hackers and their constantly developing sophisticated methods of attacks, but also keep up with the ever-changing regulatory requirements.
Some of the ways developers challenge these issues are:
- Strong authentication measures to prevent unauthorized access.the
- Making sure that data is always encrypted whether it is being transmitted or stored.
- Holding themselves accountable to stringent compliance standards
- Maintaining performance while securing complex systems
Every technical choice reflects a commitment to protecting patient information and preserving trust.
How Tekrevol Implements Encryption and Safety in Healthcare Apps
When it comes to developing medical applications with airtight security, Tekrevol approaches healthcare data security with a structured and disciplined methodology.
At Tekrevol:
- Encryption is built in from day one, covering data at rest, in transit, and during processing.
- Secure protocols and standards like TLS 1.3 and AES‑256 guide technical implementation.
- Identity and access management systems ensure only authorized users see sensitive data.
- APIs are tested and hardened using rigorous authentication and encryption practices.
- Regulatory alignment with standards like HIPAA is maintained throughout development.
By emphasizing both strong technical safeguards and regulatory compliance, Tekrevol delivers healthcare applications that protect users while providing smooth, reliable experiences.
Turn security into your competitive edge
Tekrevol builds healthcare apps with encryption at the core.
Start planning today





![How Much Would It Truly Cost to Develop a Food Ordering Website? [2026 Analysis]](https://d3r5yd0374231.cloudfront.net/images-tek/uploads/2026/03/Tek-Feature-7-1.jpg)




