There must be an app on your phone that just works the way you expect. The ease of use, smooth navigation, recommendations, and every feature match your expectations. That experience comes from backend app development, a process that often goes unnoticed but makes a huge difference.
Businesses sometimes overlook that mobile apps rely heavily on a scalable backend to function efficiently and deliver a seamless experience. According to MagicPod, testing gaps linked to backend issues cause 95% of mobile app crashes. A secure backend ensures prompt database management for the timely processing of requests, even under heavy usage.
In this guide, we’ll explain mobile app backend development with different backend types and tools. You’ll learn about popular backend app development languages and the process to integrate servers, databases, and APIs for effective backend deployment.
What Is App Backend App Development?
Mobile backend app development is the process of building server-side systems that run an app. It stores data and processes requests so the app runs smoothly.
The backend functionality is like a brain that connects apps with the frontend through API integration services to create a complete user experience. It runs the logic, stores information, and processes requests that users see and interact with at the frontend.
Messaging app like WhatsApp is the best example here. It shows your chats instantly because the backend manages accounts, stores messages, and handles notifications. By pairing mobile app development with strong backend architecture, you can make applications fast and reliable.
Behind every great app is a reliable backend.
At Tekrevol, we make it simple with custom and scalable backend app development.
Connect with Us!What Are the Key Components and Aspects of Backend App Development?
The major components of backend app development for mobiles include, but are not limited to, servers, databases, APIs, and storage. Together, these parts manage data and requests, making sure your app runs smoothly and stays secure.
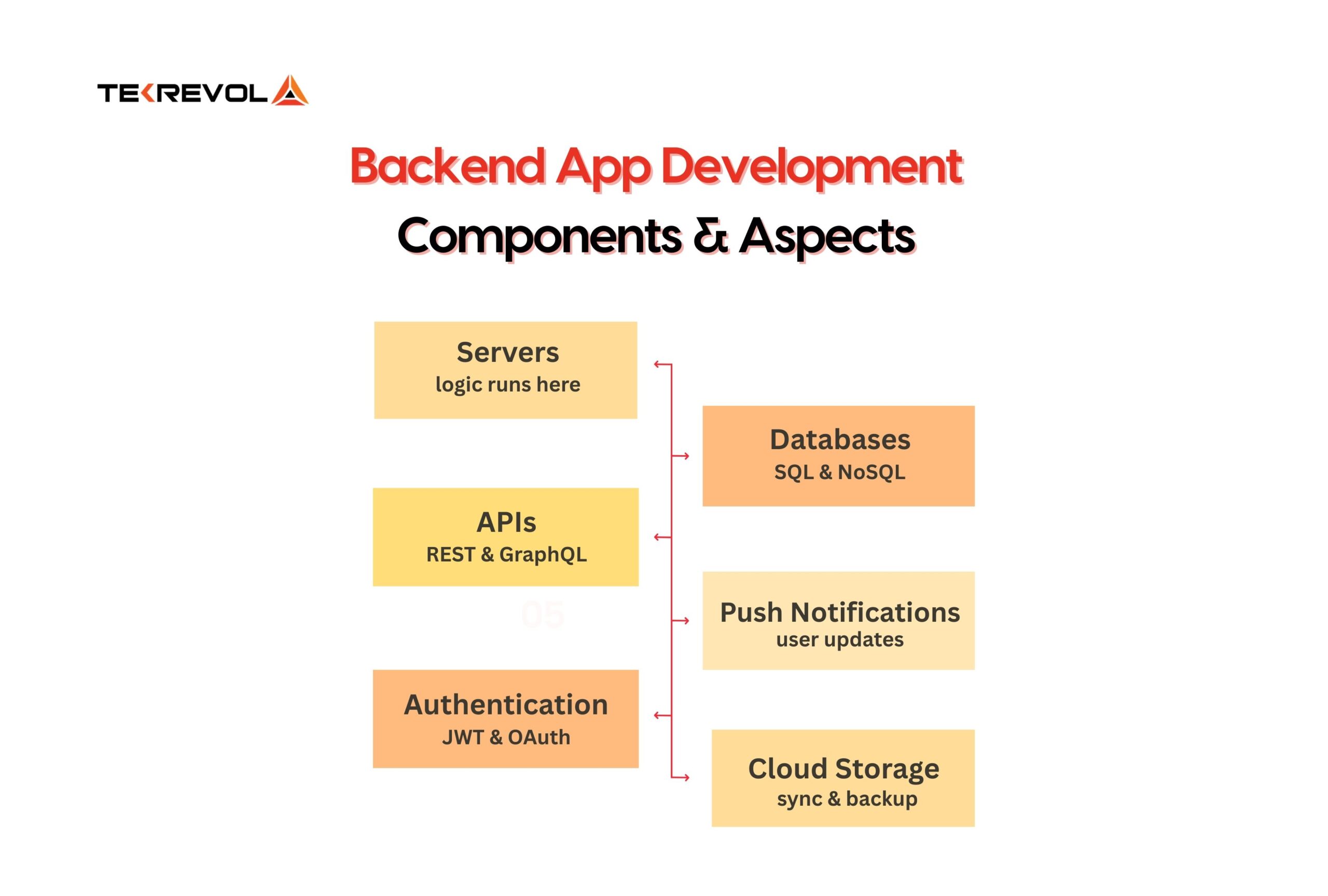
Servers
Servers are where the backend logic runs. They do the work behind the scenes, like processing requests and sending the results to the app. Without server-side development, the app cannot show information or respond to actions.
Databases
Databases are like storage rooms for the app. SQL databases like MySQL or PostgreSQL store structured data, user accounts, or orders. NoSQL databases (MongoDB) handle flexible or large data, like social media posts or app logs. The server talks to the database to get or save information whenever the app needs it.
APIs
APIs are the messengers connecting the frontend and backend. They carry requests from the app to the server and bring back the answers. Most APIs are integrated using REST for standard requests like fetching a list of products or messages. On the other hand, GraphQL APIs allow queries to flow as exactly as the data needed, which is helpful for complex apps with multiple screens or data sources.
Authentication and Security
Authentication verifies who the user is. Tools like JWT and OAuth ensure that only the right people can access accounts and sensitive information, like viewing accounts, messages, or transactions, to keep the app safe for everyone.
Push Notifications and Cloud Storage
Cloud storage is necessary for synchronizing data across devices in real time. Whereas push notifications are embedded to deliver updates or alerts instantly to users. These components keep users informed and ensure that app content is always current.
Microservices Architecture
Many apps also use a microservices architecture to divide backend workflow and functions into smaller, independent pieces. Each service handles a single task, like processing payments or sending notifications.
Frontend vs Backend App Development: How They Differ?
Frontend development focuses on the things that users see and interact with. Whereas the backend makes that possible by responding to requests and keeping the app functional. Both are required for apps to work correctly and smoothly.
| Aspect | Frontend | Backend |
| Purpose | User interface and experience | Data processing and app logic |
| Skills / Tools | HTML, CSS, JavaScript, Angular | Java, Python, Node.js, SQL, NoSQL |
| Operation | Client-side | Server-side |
| Interaction | Directly with users | Supports frontend requests |
| Focus | Smooth navigation, responsive design | Fast processing, reliable data handling |
| Security | Basic input validation | Authentication and access control |
| Updates | Visual changes, layout adjustments | Backend logic, database updates |
| Testing | UI testing, cross-browser testing | Load testing, API testing |
Knowing the difference between frontend vs backend helps you efficiently choose the right backend and frontend development framework. The decision later ensures the app looks and performs as intended while working seamlessly with the backend.
Major Types of Backend App Development
Mobile apps have different backend types depending on their needs. Custom backends provide full control and scalability. Backend-as-a-Service and cloud or third-party backends offer faster deployment with less setup effort.
Each type offers different trade-offs that affect performance and maintenance. Your app’s purpose, timeline, and budget help you find the answer to which backend is best for app development.
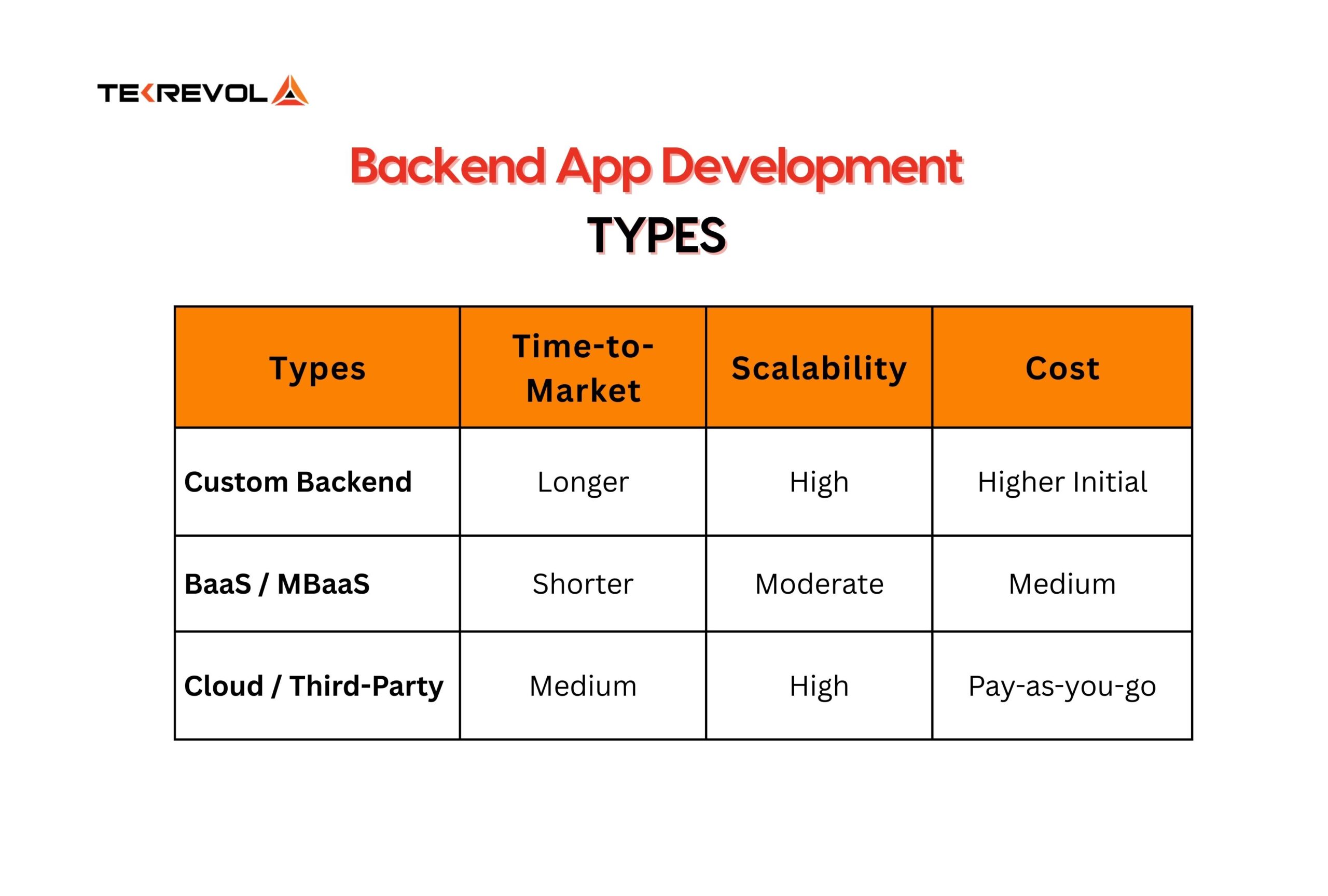
Custom Backend
Custom backend designs specifically for an app’s requirements. They give developers complete control over databases, APIs, and performance. This approach works for apps with unique features or high user traffic where scalability and security are critical.
Backend-as-a-Service
BaaS platforms like Firebase and AWS Amplify are ideal for simpler apps or projects that need quick deployment, as they provide ready-made backend tools. They manage authentication, data storage, and server logic. Developers can launch apps faster, without building everything from scratch.
Cloud or Third-Party Backends
Cloud platforms such as Azure or Heroku host your backend in the cloud. They reduce the need for manual server management and make scaling easier. Costs increase as usage grows, but proper cloud support and maintenance allow apps to handle sudden traffic spikes efficiently.
What Are the Best Backend Languages for App Development
Backend languages define how the server processes data, manages databases, and communicates with the frontend. While Node.js, Python, Java, Kotlin, PHP, Ruby, and Go are commonly used, there is no single “best backend language for app development. The choice depends on your app’s type, features, and scalability needs.
Node.js (JavaScript / TypeScript)
Node.js works best for real-time chat apps or collaboration tools. Using it, developers can work with JavaScript or TypeScript on both the frontend and backend. This creates a consistent development environment to handle concurrent requests efficiently.
Python (Django / Flask)
Python frameworks such as Django and Flask are widely used for scalable apps and machine learning integration. They simplify development with readable code and extensive libraries. Python is especially popular when building apps that need data processing or AI features.
Java / Kotlin
The use of Java and Kotlin is more common in enterprise applications and Android apps owing to their strong typing and high performance. These languages work well for apps that require heavy computation or long-term maintenance.
PHP / Laravel, Ruby on Rails, Go
PHP with Laravel is suited for small to medium web apps. Ruby on Rails speeds up development with convention-based practices. Go provides high performance for apps that need fast processing and scalability. Each language fits specific use cases and developer expertise.
Technology Stack and Tools for Mobile App Backend Development
A backend technology stack is the set of frameworks, databases, APIs, and tools that form the foundation of any mobile app. It also affects development speed and long-term maintenance. Working with the right backend app development tools and stack keeps your app reliable with users.
Frameworks
Frameworks simplify backend coding by providing prebuilt structures and patterns. Express.js works well with Node.js for fast and lightweight apps. Django is a strong choice for Python-based projects requiring scalability. Spring Boot suits Java applications with complex logic, and Laravel is popular for PHP-based apps. Using the right framework improves code quality and reduces development time.
Databases
Databases store and organize app data. PostgreSQL and MySQL are relational databases (ideal for structured data). MongoDB and Firebase DB handle unstructured or real-time data efficiently. Selecting a database depends on speed, scalability, and real-time updates of an app.
APIs
APIs connect the backend with the frontend and external services. REST APIs are widely used and simple to implement. GraphQL allows clients to request only the data they need, reducing overfetching and improving performance. Choosing the right API style impacts efficiency and scalability.
Tools
Development tools streamline collaboration and testing. GitHub manages version control and code sharing. Docker helps containerize apps for consistent deployment. Postman and Swagger assist with API testing and documentation. Monitoring tools like Datadog and New Relic track app performance and detect issues early.
The latest backend technology stack layers frameworks and databases with APIs and these tools. You can explore backend app development GitHub repositories to see real-world implementations and best practices.
Your backend stack shapes app performance.
Tekrevol uses proven tools and frameworks to design a backend that works for your business.
Connect With Us TodayHow to Make a Backend for an App?
You can do backend development by following these steps which begin with language and framework selection. The next step involves servers and databases. Then you create APIs and add security. Finally, you test the system to make sure the app is stable and ready to use.
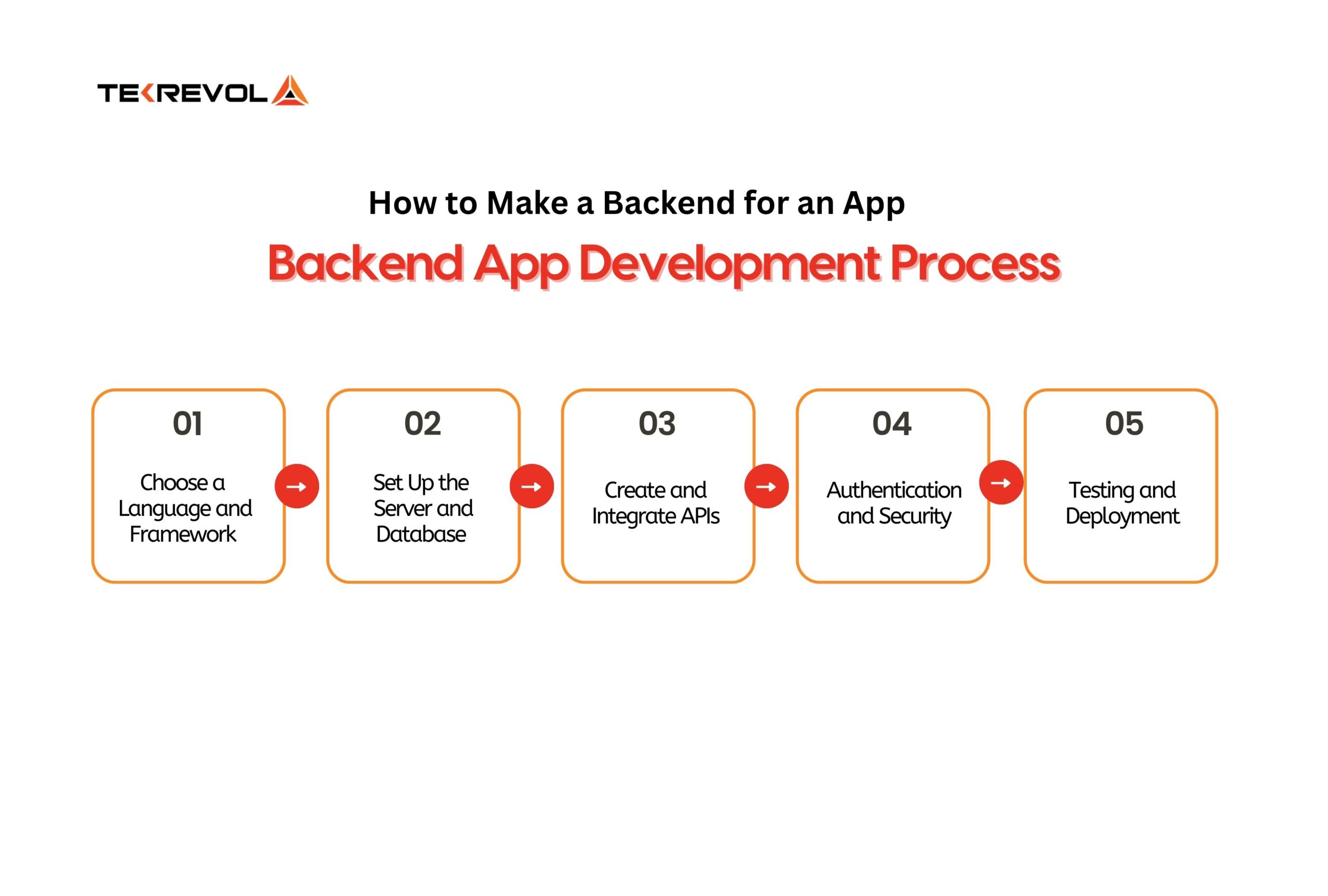
Choose a Language and Framework
Language and framework selection shape your entire build. The choice depends on the app type and the skills of the team. We recommend Node.js with Express for fast apps and Python with Django for scalable systems, or Java with Spring Boot for enterprise projects.
Set Up the Server and Database
A server processes requests while a database stores information. For example, one retail app supports PostgreSQL for structured data and Firebase for real-time sync. This mix gave the app quick updates without slowing the server.
Create and Integrate APIs
APIs let the app talk to the backend and outside services. REST works well for simple communication, while GraphQL helps when apps need custom queries. A backend app development GitHub repo often shows sample code for both.
Authentication and Security
No backend is complete without user protection. Methods like JWT tokens and OAuth secure logins. In backend app development for healthcare, strict authentication is required to meet compliance standards.
Testing and Deployment
Testing checks performance under real conditions. Tools like Postman help with APIs, and Docker makes deployment reliable. For Android backend mobile app development testing, it also ensures a smooth connection with native features.
This simple backend app development tutorial gives the roadmap. You can adapt it as per your needs and projects, like chat apps, eCommerce systems, or other backend examples. The key is to start small and test early to refine the backend as the app grows.
What Are the Common Challenges in Backend App Development
When you build a backend, you often face database scaling issues, performance slowdowns, API hurdles, and security risks. Each challenge has a solution if you catch it early.
Database Scaling Issues
If your app grows, the database may lag. You can fix this with caching, sharding, or cloud databases that expand when you need them.
Performance Bottlenecks
Slow response times frustrate users. Tools like New Relic or Datadog help you spot the cause so you can balance traffic or clean up heavy code.
API Integration Complexity
Linking APIs can feel messy. Standards differ, and bugs creep in. Using Postman for testing and middleware for translation makes the process smoother.
Security Risks
Your users trust you with their data. Protect it with encryption, OAuth, JWT tokens, and regular updates to frameworks.
How Tekrevol Backend App Development Services Assist You
By now, you get that backend app development is the foundation of a stable and scalable mobile app. Every layer, from servers and databases to APIs and security infused together to make the user experience smooth and reliable.
Thus, choosing the right type of backend, programming language, and technology stack is not just a technical step but a business decision that affects performance and growth. At Tekrevol, our role is to turn those choices into practical backend solutions.
With experience in backend mobile app development and knowledge of both SQL and NoSQL databases, we design systems that adapt to future needs as well as current goals.
Our team uses agile practices, modern stacks, and proven workflows to handle challenges such as scaling databases or integrating APIs. That expertise allows us to match the backend solution to the long-term goals of each project.
Strong backends build stronger apps.
TekRevol helps businesses launch and scale apps with reliable infrastructure.
Talk to backend experts now.










