As voice is becoming the new interface, understanding “what is speech recognition” proves a key to unlocking smarter interactions with technology.
Simply put, speech recognition allows computers and devices to understand, process, and respond to human voice commands. From virtual assistants like Siri and Alexa to Windows speech recognition and automatic transcription tools, the technology is revolutionizing how we work, communicate, and control devices.
With the rise of speech recognition software in smartphones, computers, and AI-driven apps, users can dictate text and even navigate systems hands-free. In 2025, over 78% of smartphone users globally are interacting with voice assistants daily, according to AI Radar, proving just how mainstream this tech has become.
Whether you’re curious about what is speech recognition in AI or exploring practical speech recognition examples, one thing is sure: this technology is shaping the future of human-computer interaction.
So, let’s look at “what is speech recognition” in this guide and find your answers to how it works, and how to use speech recognition to build inclusive, voice-first applications.
What is Speech Recognition?
In simple terms, it’s the technology that lets computers understand your voice. It converts spoken words into text or commands that a device can act on.
While the answer to “what is speech recognition?“ sounds simple, behind the scenes, it involves analyzing sound waves, recognizing patterns, and generating responses in real time.
Whether you’re talking to a smartphone, wearable apps, or even a smart speaker, speech recognition software interprets your voice and carries out tasks. This can include setting alarms, transcribing voice notes, or even translating speech on the fly.
Why Speech Recognition Technology Matters for App Developers
For developers and businesses, speech recognition technology opens the door to:
- Improved accessibility for people with physical disabilities or visual impairments.
- Frictionless interfaces in mobile apps, where typing may be cumbersome.
- Smarter AI integrations via conversational interfaces.
- Multilingual input capabilities help apps cater to global audiences.
Industries Using Speech Recognition
- Healthcare: Over 68% of hospitals in the US now use speech-to-text software for real-time clinical documentation, improving accuracy and saving doctors up to 2 hours daily (Source: HIMSS 2025).
- Education: With the rise of hybrid learning, voice recognition tools are being used in over 75% of digital classrooms to transcribe lectures and support students with disabilities (Source: EdTech Review 2025).
- Retail: According to TIQ Digital, voice-based shopping is expected to exceed $60 billion globally in 2025, with major retailers integrating voice search into mobile apps for faster browsing.
- Automotive: Nearly 85% of new vehicles in 2025 come equipped with speech recognition systems, enabling drivers to control navigation, music, and calls hands-free (Source: McKinsey Mobility Report 2025).
- Finance: Banks are embracing voice biometrics and speech interfaces, with 43% of consumers now using voice command features of mobile banking apps for tasks like transfers, bill payments, or checking balances.
Applications of speech processing aren’t just a novelty anymore; it’s a necessity in modern app development.
How Speech Recognition Works
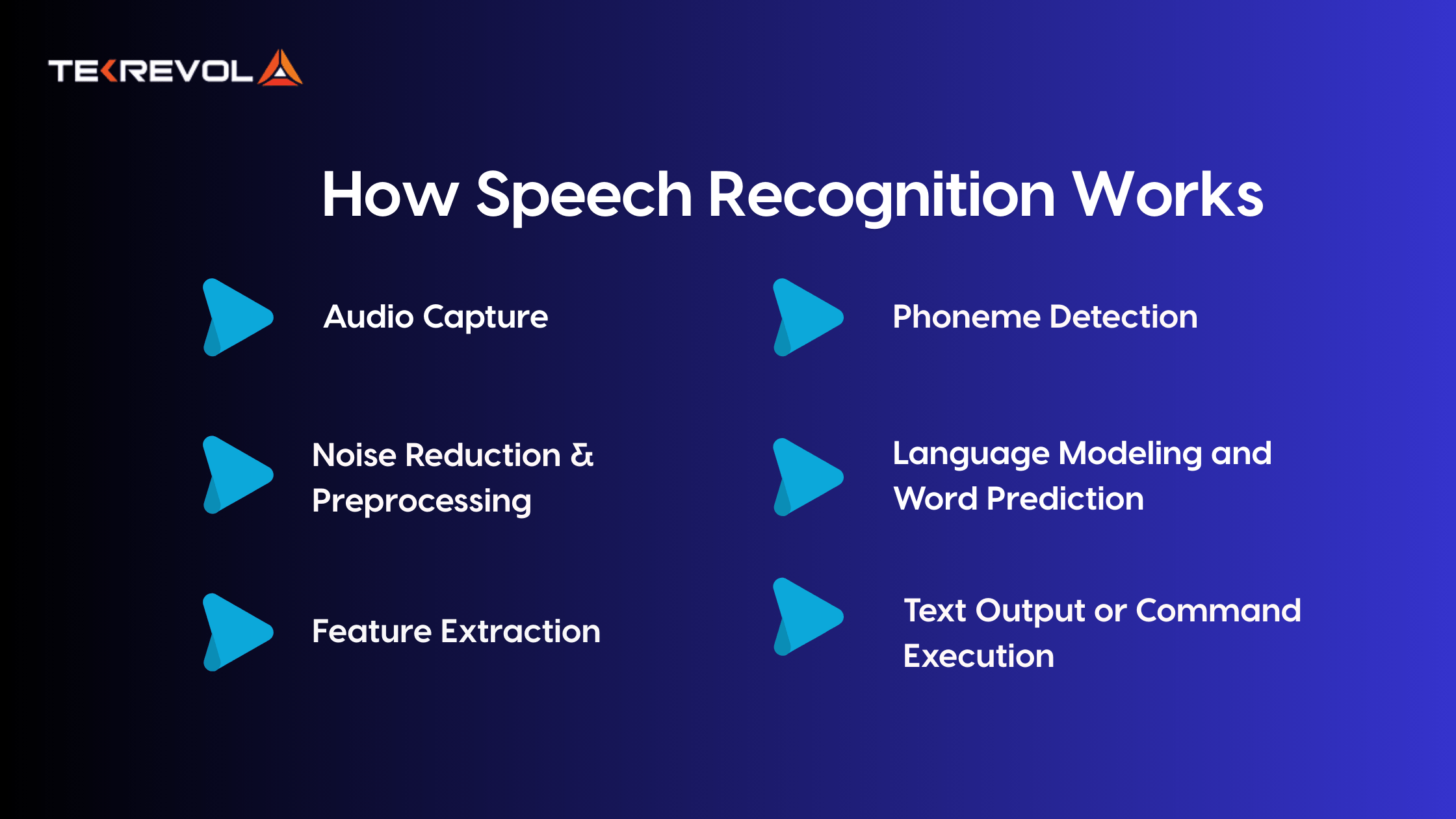
Despite knowing what is speech recognition, many consider it an effortless, instant process. No, it is a multi-stage pipeline. Let us dissect the applications of speech processing by which speech data is captured, processed, and interpreted.
1. Audio Capture
Recording the user’s voice through the device’s microphone is the starting point. Analog sound waves are then transformed into digital signals that can be processed by software.
2. Noise Reduction & Preprocessing
The environment is seldom silent. That’s why speech recognition systems use acoustic filtering and noise reduction algorithms to pick out the speaker’s voice from ambient noise.
3. Feature Extraction
The system then detects important patterns in the sound with Fourier transforms or MFCCs (Mel-Frequency Cepstral Coefficients)—a model of the frequency content of the audio signal. This phase extracts speech features like pitch, duration, and intensity.
4. Phoneme Detection
The audio components are broken down to identify phonemes, the building blocks of speech (such as “sh,” “b,” “ah”). Imagine this as translating sound waves into Legos that can be built into words.
5. Language Modeling and Word Prediction
Through statistical models or neural networks, the software then estimates the most likely words that are spoken by the sequences of phonemes. This involves the utilization of contextual evidence from preceding words or typical phrases to maintain accuracy.
6. Text Output or Command Execution
Finally, the recognized speech is converted into text or directly executed as a command, triggering anything from playing music to sending an email.
This entire chain happens in milliseconds, powered by cloud computing and edge AI integration to mobile applications.
- Want fewer clicks and more wow-factor
- Let speech recognition do the heavy lifting while your app gets all the praise.
Types of Speech Recognition Systems
When you want to understand what is speech recognition, do not forget to look into the types of systems available. The knowledge comes in handy to compare kinds of speech recognition systems and choose the right one to ensure your app delivers accurate and efficient voice interaction.
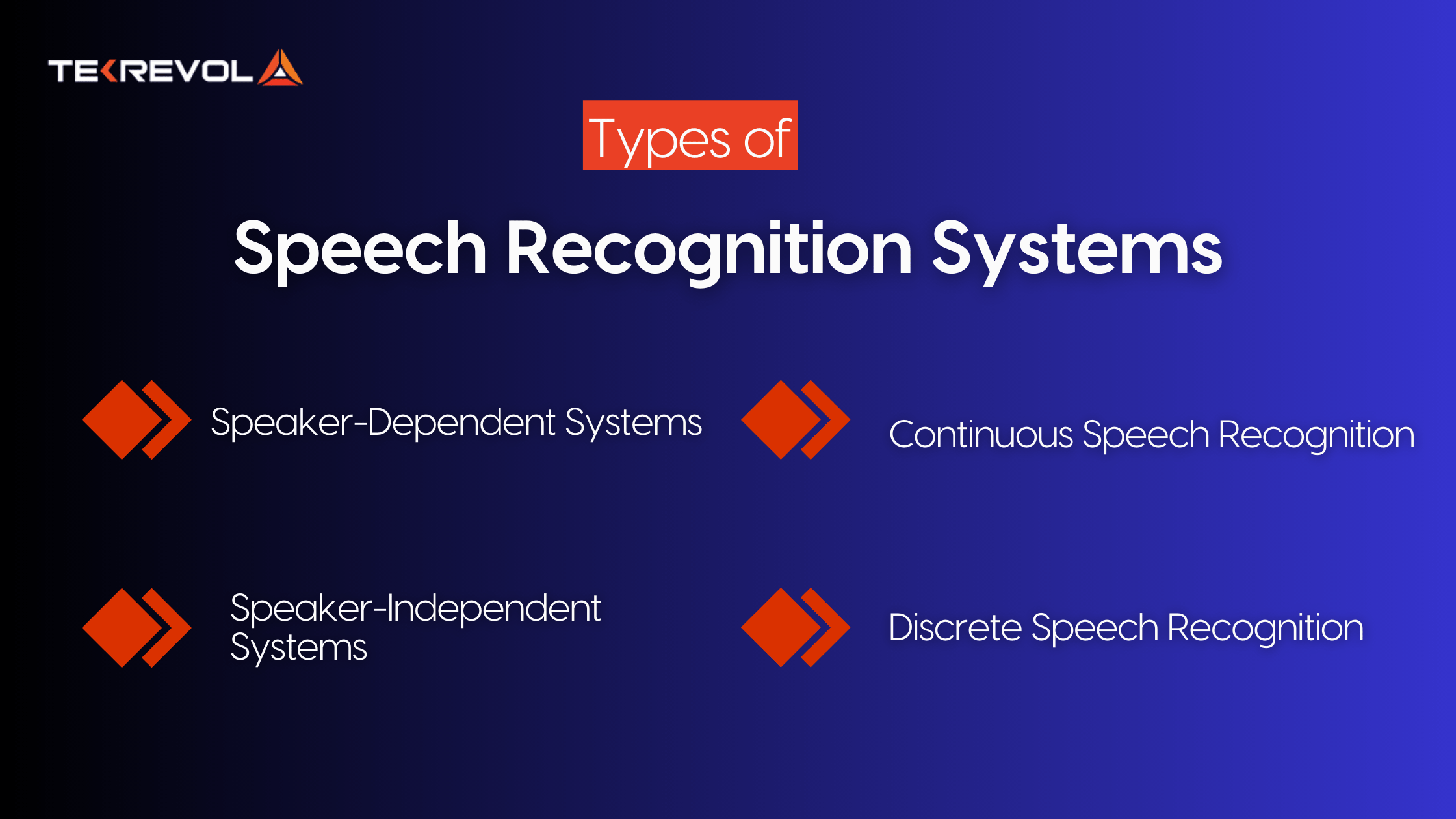
1. Speaker-Dependent Systems
These systems learn a specific user’s voice and speech patterns. Often used in personal assistants and secure voice authentication, they offer high accuracy but require initial training.
2. Speaker-Independent Systems
Designed to recognize speech from any user, these are ideal for public-facing mobile app development and customer support bots. They rely on large datasets to generalize across accents, genders, and vocal tones.
Comparison Table between Speaker-Dependent and Speaker-Independent Systems
| Feature | Speaker-Dependent | Speaker-Independent |
| Accuracy | High (after training phase) | Moderate to High (depends on dataset size) |
| User Personalization | Tailored to one voice | Works across many voices |
| Training Requirement | Yes (initial voice training needed) | No training required |
| Ideal Use Case | Voice authentication, personal assistants | Customer service bots, public interfaces |
3. Continuous Speech Recognition
Modern speech recognition software can process natural, flowing speech at varying speeds and tones. It powers dictation apps, transcription-oriented AI productivity tools, and voice search features.
4. Discrete Speech Recognition
An older form where users need to pause between words. While mostly outdated, some niche applications still use it for enhanced accuracy in noisy environments.
Each model serves a specific purpose, so align your app’s function with the appropriate system.
Comparison Table between Discrete and Continuous Speech Recognition
| Feature | Discrete Speech Recognition | Continuous Speech Recognition |
| Speaking Style | Word-by-word with pauses | Natural, flowing speech |
| Speed | Slower | Faster and more conversational |
| Use Cases | Noisy environments, niche tools | Dictation apps, voice search, and assistants |
| Modern Relevance | Rarely used | Common in today’s applications |
Key Features of Speech Recognition Technology
Developers must comprehend the basic components of speech recognition systems in order to create scalable, reliable speech-enabled applications.
1. Acoustic Model
This model connects sound signals to phonemes. It’s trained on thousands of hours of speech and learns how different voices produce the same phoneme.
2. Language Model
It uses probabilities to predict word sequences. For instance, “read a book” is more likely than “read a back,” even if the sounds are similar.
3. Pronunciation Dictionary
Acts as a bridge between phonemes and the actual written words. It helps the software understand that the phoneme sequence /r/ /ɛd/ corresponds to “read.”
4. Decoder Algorithm
The decoder takes input from the acoustic and language models and determines the most probable output.
5. NLP Layer (Natural Language Processing)
Natural Language Processing adds another layer by interpreting meaning, context, sentiment, and intent. It enables voice assistants not just to transcribe speech, but to respond intelligently.
Common Applications of Speech Processing in Apps
Understanding “what is speech recognition” becomes easier when you see its practical uses. Speech recognition technology is driving innovation across multiple app categories, making interactions faster, smarter, and more accessible.
1. Voice Search and Navigation
eCommerce apps use voice search to make browsing more intuitive. Commands like “find black sneakers under $50” or “navigate to the nearest café” let users interact without typing.
2. Real-Time Transcription
Apps like Otter.ai help journalists, students, and podcasters capture and convert spoken words into editable text with time stamps and speaker identification.
3. Chatbots and Virtual Assistants
From banking to healthcare, conversational AI bots increasingly rely on speech input, enhancing automatic speech recognition for seamless, human-like interactions.
4. Improvements in Accessibility
Voice-to-text and voice navigation allow users with mobility or visual impairments to operate apps independently, making speech recognition systems crucial for inclusive design.
5. Voice Control in Workplace Applications
Voice dictation is being integrated into task management applications like Notion, Evernote, and Google Docs to streamline the content creation process for notes, memos, and even emails.
Advantages of Implementing Speech Recognition in Mobile Apps
Implementing speech recognition is not just a technical upgrade—it’s a user experience transformation. Here’s why:
1. Hands-Free Convenience
The ability for users to engage with your app while multitasking, cooking, driving, or working out improves usability in practical situations.
2. Faster Data Input
Speaking is faster than typing, especially on mobile devices. This makes speech ideal for quick notes, voice searches, or form filling.
3. Inclusivity and Accessibility
People with impairments will find your software easier to use, increasing its user base and guaranteeing compliance with accessibility regulations.
4. Higher User Engagement
Voice interfaces feel personal and conversational. This leads to deeper engagement and improved user retention.
5. Global Reach
Speech recognition systems can be multilingual, enabling your app to reach users in multiple languages and dialects.
Popular Speech Recognition Software and APIs
You don’t have to build everything from scratch. Here are the most widely used APIs for speech recognition integration:
1. Google Cloud Speech-to-Text
Supports over 120 languages and offers real-time streaming transcription, speaker diarization, and word-level timestamps. Great for global apps.
2. Microsoft Azure Speech Service
Features include real-time transcription, speaker recognition, and translation. Azure also offers excellent SDKs for mobile and IoT.
3. Amazon Transcribe
Amazon Transcribe is best for media and enterprise use cases with support for automatic punctuation, custom vocabulary, and call analytics.
4. IBM Watson Speech to Text
Known for high accuracy in noisy environments. Offers great integration with Watson NLP and tone analyzers.
5. AssemblyAI
A fast-growing API provider with advanced features like sentiment analysis, keyword spotting, and topic detection—useful for rich AI integrations.
- Want to Integrate Advanced Speech Recognition into your App
- At Tekrevol, we bring your voice-powered idea to life with cutting-edge speech recognition
Challenges in Speech Recognition Technology
Despite its success, voice recognition app development still faces several challenges that developers must work around:
1. Accents, Dialects, and Multilingual Variations
Training models to handle various accents or switch languages mid-sentence remains complex and can reduce accuracy.
2. Noisy Environments
Recognizing speech in cars, cafes, or crowded events is still problematic. While noise-cancellation techniques help, results vary.
3. Homophones and Word Ambiguity
Words like “to,” “too,” and “two” sound identical but have different meanings. NLP services help here, but it’s not foolproof.
4. Real-Time Performance
Ensuring low latency in mobile or edge environments can be technically demanding, especially for real-time applications like live subtitles or dictation.
5. Privacy and Security
Handling sensitive user voice data raises GDPR, HIPAA, and general privacy compliance concerns. Encryption, anonymization, and consent mechanisms are essential.
What is the Purpose of ASR?
A branch of speech technology designed to work as an automatic transcription of words into written form without the involvement of any human is known as Automatic Speech Recognition.
These ASR systems include the usage of deep learning and machine learning frameworks like RNNs, LSTMs, and transformers to decode speech functionality with context awareness.
What makes ASR particularly powerful is:
- End-to-end training with massive datasets.
- Self-learning capabilities that improve over time.
- Real-time transcription, even in streaming audio environments.
ASR is the engine behind transcription services, dictation tools, and real-time communication platforms.
Windows Speech Recognition: A Built-In Option
For developers exploring “what is speech recognition”, Microsoft’s native Windows Speech Recognition (WSR) provides a practical starting point on Windows platforms.
It offers:
- Voice commands to control Windows features and applications.
- Dictation tools for Word, email, and browser input.
- Custom command creation for niche use cases.
While Windows speech recognition may not match advanced cloud-based APIs, it remains a valuable tool for prototyping, offline voice control, and accessibility testing. Integrating WSR can help understand core speech recognition systems before scaling to more complex AI or automatic speech recognition solutions.
Wrap Up
Now you know “what is speech recognition” and how it’s powering the future of hands-free tech, from simplifying healthcare workflows to transforming the way users shop, bank, and learn. If you’re planning to build one, understanding the speech recognition app development cost can help you make smarter product decisions from the start.
At TekRevol, we specialize in building voice-enabled apps tailored for tomorrow’s user expectations. Our experience spans across industries, healthtech, edtech, fintech, and beyond—helping clients deliver intuitive, hands-free solutions.
Why Choose TekRevol for Speech/Voice Recognition App Development?
- Expertise in Google, Amazon, and Azure speech APIs
- Custom NLP and AI integrations
- Scalable infrastructure for high-volume usage.
- Focus on privacy-first architecture
- Deep understanding of UI/UX for voice interaction
Whether you’re launching a conversational AI bot, a voice-dictation mobile app, or an accessibility-focused tool, TekRevol is your strategic partner in voice recognition app development and innovation.
- Ready to Give Your App a Voice of Its Own
- From smarter accessibility features to voice-powered assistants, we have the expertise to turn your idea into a voice-enabled reality.







![What is Visual Regression Testing [2025 Definitive Guide]](https://d3r5yd0374231.cloudfront.net/images-tek/uploads/2025/11/Feature-19.jpg)



